You may have heard of cortisol being referred to as the “stress hormone.” This is because it plays a crucial role in our biological response to stress. However, it’s important to note that cortisol is not solely a negative hormone. In fact, it serves as a key player in many of our body’s functions and systems.
Despite its negative connotation, cortisol is essential to our overall health. It helps regulate our blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and immune system response. Let’s look at the various functions of cortisol and how it affects our body.

What Is Cortisol and What Does It Do?
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that plays a crucial role in the human body. It regulates metabolism, reduces inflammation, assists with memory formation, and manages stress. In an emergency or frightening situation, the adrenal glands secrete more cortisol into the bloodstream, increasing heart rate and blood pressure in anticipation of a threat. This is the body’s natural “flight or fight” response when it detects something amiss to prepare you either to avoid (flee) or confront (fight) the danger.
While cortisol is essential for survival, excessive cortisol in the bloodstream can be harmful to both physical and mental health. When your system produces too much cortisol or never returns to a state of homeostasis, you may experience chronic stress.
Symptoms of high cortisol levels include weight gain, anxiety, depression, increased blood pressure, and decreased immune function. It is crucial to manage cortisol levels to avoid long-term stress and its harmful effects.
There are several strategies to lower cortisol levels naturally, including exercise, meditation, deep breathing, and getting enough sleep. By incorporating these techniques into your daily routine, you can reduce cortisol levels and alleviate the effects of chronic stress on your body and mind.

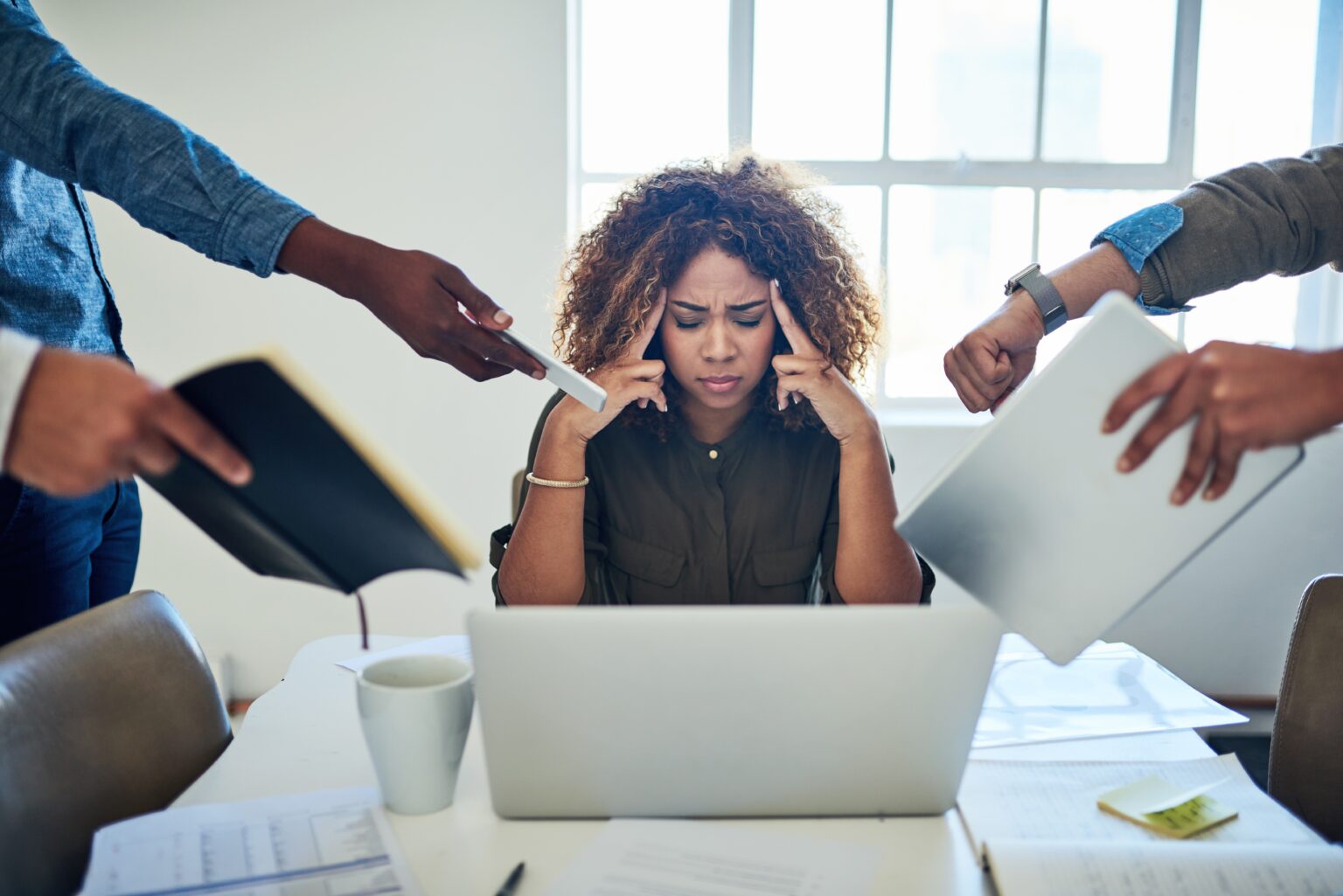
Signs of High Cortisol Levels
If you are experiencing chronic stress, it may lead to high cortisol levels, which can cause a range of symptoms. Here are some signs that you may have high cortisol levels:
- Disrupted sleep: High cortisol levels can make it difficult for you to fall asleep or stay asleep. You may also experience nightmares or vivid dreams.
- Muscle weakness: Elevated cortisol levels can interfere with the way your body processes protein and carbohydrates, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue.
- Anxiety: High cortisol levels can cause anxiety, irritability, heart palpitations, and shortness of breath.
- Memory impairment and difficulty concentrating: Chronic stress can affect your ability to recall information and concentrate on tasks.
- Frequent colds: High cortisol levels can suppress your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Irritable bowel syndrome: Stress can affect the gut-brain axis, leading to digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome.
- Hirsutism or excessive hair growth in females at birth: High cortisol levels can stimulate hair follicles, leading to excessive hair growth in females.
It’s important to note that the severity and effects of high cortisol levels vary from person to person. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s recommended that you consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment plan. Additionally, incorporating stress-reducing habits into your daily routine such as exercise, meditation, and getting adequate sleep can help regulate cortisol levels and improve overall health.
Effects of Long-Term High Cortisol Levels
Long-term high cortisol levels can have adverse effects on various hormone processes in the body, which can lead to serious health consequences. Here are some of the effects of long-term high cortisol levels:
- Decreased Libido: High cortisol levels can lead to adrenal fatigue and a lack of sex drive. The adrenal glands may no longer produce enough cortisol, which can contribute to decreased libido.
- Irregular or Stopped Periods (Amenorrhea): Chronic stress can lead to irregular menstrual cycles and amenorrhea. The secretion of more endorphins and cortisols during stress can interrupt ovulation and appropriate hormone production.
- Mental Health Struggles: Chronic stress is associated with several psychological issues, including anxiety and depression. Excessive pressure and lack of resolution may also raise the risk of relying on substances like illegal drugs and alcohol as coping mechanisms.
It is important to manage stress levels and maintain a healthy cortisol balance to avoid these negative effects on the body.
Long-Term Habits to Lower Cortisol Naturally
If you’re looking for ways to lower your cortisol levels naturally, there are several long-term habits that you can adopt. These habits can help you manage stress, improve your overall health, and promote a healthy balance of cortisol in your body. Here are six effective habits to consider:

1. Get Sufficient Sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial for regulating cortisol levels in your body. Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep per night to ensure that your body has enough time to rest and recover. If you’re having trouble sleeping, try establishing a consistent sleep routine, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and creating a relaxing sleep environment.

2. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise is a powerful stress reliever that can help lower cortisol levels in your body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. This can include activities like brisk walking, yoga, or dancing. Exercise can also improve your sleep quality and promote the release of feel-good chemicals like serotonin and endorphins.

3. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and tai chi can help lower cortisol levels significantly and promote overall health. These practices can help you shift from fight-or-flight mode to rest-and-digest mode, lower your heart rate and blood pressure, and reduce stress and anxiety.

4. Learn Your Stressors
Identifying the things that stress you out can help you manage your stress more effectively. Whether it’s physical or psychological stress, understanding your stressors can help you develop coping strategies and reduce your cortisol levels. Take note of the situations or activities that trigger your stress response and try to avoid or minimize them whenever possible.

5. Find a Hobby That Makes You Happy
Engaging in pleasurable hobbies that calm you down, distract you in a healthy way, and lift your mood can be highly therapeutic for stress management and reduction. Creative and artistic activities like drawing, painting, music, and dance can be particularly effective. These hobbies can promote relaxation, reduce cortisol levels, and lower depressive symptoms.

6. Nurture Healthy Relationships
Strong social connections are crucial for stress resilience and overall mental well-being. Surround yourself with supportive and positive people who lift you up and help you manage stress effectively. Let go of toxic relationships or set healthy boundaries with people who cause you stress. Nurturing healthy relationships with loved ones, volunteering, or joining a club can also help you feel supported and connected.
By adopting these long-term habits, you can lower your cortisol levels naturally and improve your overall health and well-being. Remember that stress is a normal part of life, but if it starts to affect your relationships, physical and/or mental health, and quality of life, it’s important to seek help from a healthcare professional.